The bulk-base chemiosmotic theory cannot account for ATP production in alkaliphilic. Free energy change during movement across a proton gradient Proton-motive force Dp is a Dy- or DE-like term DE is electromotive force that combines the concentration and voltage effects of a proton gradient such that DG - nFDp 0 nFDp and Dp 0 0 proton motive force 0 under std conds so.
The Proton Motive Force Dummies
Chemicalcontribution G chem nRT ln H in H out n number of protons translocated p - 0059 V pH p - 017 - 003 - 020 V 2.
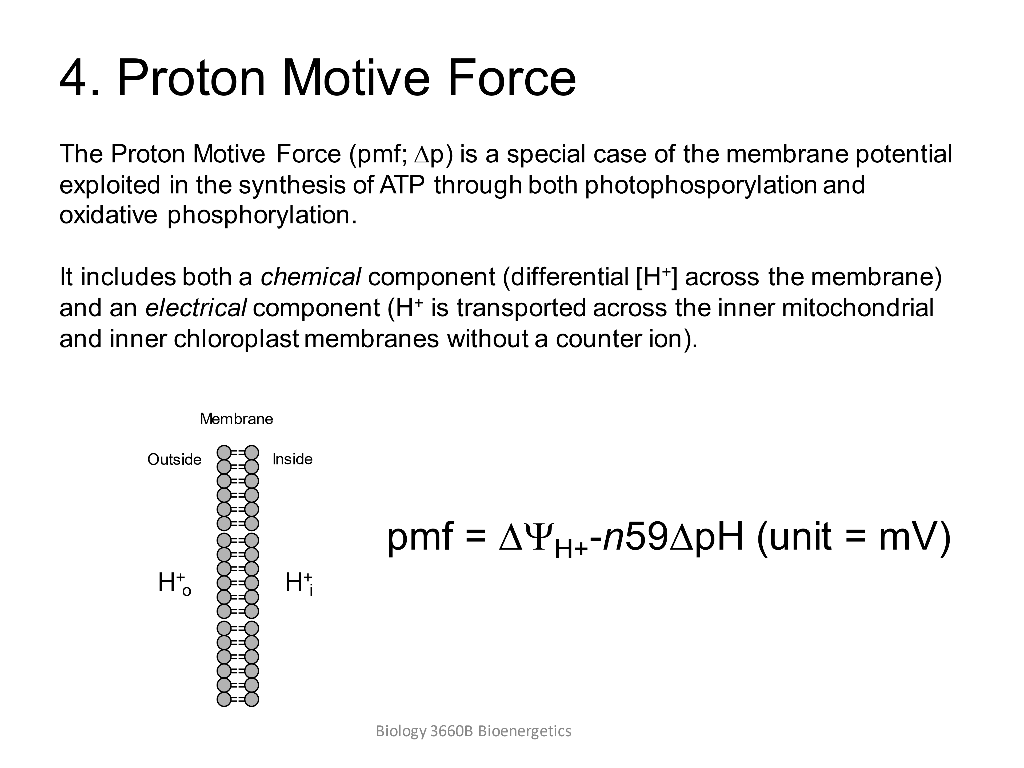
Proton motive force equation. Note on symbols The symbol normally used for electrochemical potential is read as mu bar. To emphasize this crucial role of the proton motive force the equation for ATP synthesis is sometimes written as. The energy expressed here as Gibbs free energy electrochemical proton gradient or proton-motive force PMF is a.
ADP Pi n H P ----- ATP H 2 O nH N. H elektrochemischer Protonengradient. Remember this is a recording that pH pH in - pH out and Dy m y in - y out.
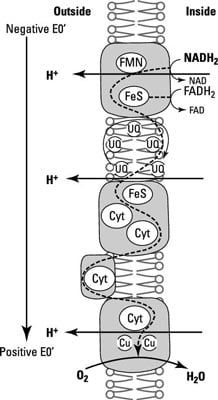
One way the proton motive force begins is with the donation of H from NADH to flavin mononucleotide FMN to make FMNH 2. Equations for transport of protons. The Protonmotive Force Protonmotive force p is the energy of the proton concentration gradient.
B It takes about four protons to make one ATP from ADP. Although rodent brown adipose tissue mitochondria are unusually well endowed with a high capacity to degrade and. Because it is not easy to generate this symbol in HTML I have used m instead The equilibrium condition A case of special interest is the equilibrium state for the transport of an ion down a.
To demonstrate the fundamental behavior of localized protons in a pure water- membrane-water system in relation to the. H 1 kJmol corresponds to p 104 mV. Equations The proton-motive force is derived from the Gibbs free energy.
Metabolic processes maintain this gradient by pumping protons across the cell. Die physikochemische Beschreibung der protonenmotorischen Kraft gibt folgende Gleichung wieder. The proton-motive force created by the pumping out of protons by the respiratory chain complexes is in the mitochondria of most tissues mainly used to translocate protons through the ATP synthase complex leading to the formation of ATP from adenosine diphosphate ADP and phosphate.
The proton motive force has two possible beginnings. At 25 C 298K this equation takes the form. First the electrical component is caused by a charge difference across the lipid.
Hout-- Hin the proton-motive force can be written as the difference between the inside and outside chemical potentials for H. DG - 2303 RT DpH nF Dy m. Mitchell defined the proton-motive force PMF as.
PHout and 2303RTF 60 mV at 300 K 27 oC. The typical pH difference is roughly 1 about 77 inside and 70 outside. The widespread Mitchellian proton motive force equation has recently been revised with the proton-electrostatics localization hypothesis which for the first time successfully elucidates the 30-year longstanding energetic conundrum of ATP synthesis in alkalophilic bacteria.
4H move to the outside of the cell when FMNH 2 donates 2e to the FeS proteins in complex I. G is the Gibbs free energy change during transfer of 1 mol of cations Xm from the phase A to B down the electrical potential is the electrical potential difference mV between phases P and N A and B A and B are our cation concentrations on opposite sides of the membrane F is the Faraday constant R gas constant. Under specific growth conditions at 27oC 300 Kelvin the pH of the medium is 70 and the pH of the cytoplasm is 75.
During this process protons are transferred from the stroma into the thylakoid lumen which generates a proton motive force pmf across the thylakoid membrane 1 2. Plant photosynthesis generates reducing power in the chloroplast stroma. This potential energy is used for the synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation or photophosphorylation respectively.
This force drives the translocation of protons across the membrane to perform chem-ical osmotic and mechanical work 3. The equation for proton motive force pmf or is where is the membrane potential in mV pHin. Mitchell used chemiosmotic to describe enzymatic reactions that involve simultaneously a chemical reaction and a transport process.
Proton-motive force a Use Equation 1861 to make an estimate of the contribution of the mathrmH concentration gradient to the proton-motive force in a cell. DG nF Dp. Coli cells accumulate the sugar lactose in its cytoplasm by a proton H symport mechanism.
In Mitchells chemiosmotic theory a proton H motive force across the membrane p generated by the respiratory chain drives F1Fo-ATPase for ATP production in various organisms. Often called the proton motive force pmf measured in volts. G Hi - Ho RTlnH i H o zF i - o.
An electrochemical gradient has two components. Motion is the generation of the proton-motive force PMF an electrochemical gradient that is maintained across the cell membrane by metabolic processes. H p 23 RTF pH.
p protonenmotorische Kraft. If the free energy needed is in the range 20. This way of expressing the proton-motive force was probably adopted because of its elegant resemblance to the Nernst equation but the clearest expression of the energy available from a proton gradient is probably.
In mitochondria and chloroplasts proton gradients are used to generate a chemiosmotic potential that is also known as a proton motive force.

Solved 9 The Proton Motive Force Write A Simple Chemical Chegg Com

The Proton Motive Force In Mitochondria Ap Can Be Chegg Com

7 The Proton Motive Force In Mitochondria Ap Can Chegg Com
2 Mitochondrial Vs Chloroplastic Pmf A In Chegg Com

Chapter 14 Part 2 Oxidative Phosphorylation Proton Motive Force P Pmf Is The Energy Of The Proton Concentration Gradient The Chemical Ph Ppt Download

By Annette Von Drygalski And John W Adamson Ppt Download
Plant Physiology And Development Sixth Edition

Passive H Flux Across The Plasma Membrane Is Governed By The Proton Download Scientific Diagram

Bio 402 502 Advanced Cell Developmental Biology I Section I Dr Berezney Ppt Download
Plant Physiology And Development Sixth Edition
Http Epgp Inflibnet Ac In Epgpdata Uploads Epgp Content S000002bi P000982 M017762 Et 1495006175e Textmodule 17 Protonmotiveforce Pdf

Electron Transport Chemiosmotic Theory Electron Transport Electrons Carried

C11 Proton Gradient Collapse And Atp Synthesis Thermodynamics Biology Libretexts

110 Proton Motive Force Youtube
Chemiosmotic Coupling Part 1 Molecular Biology
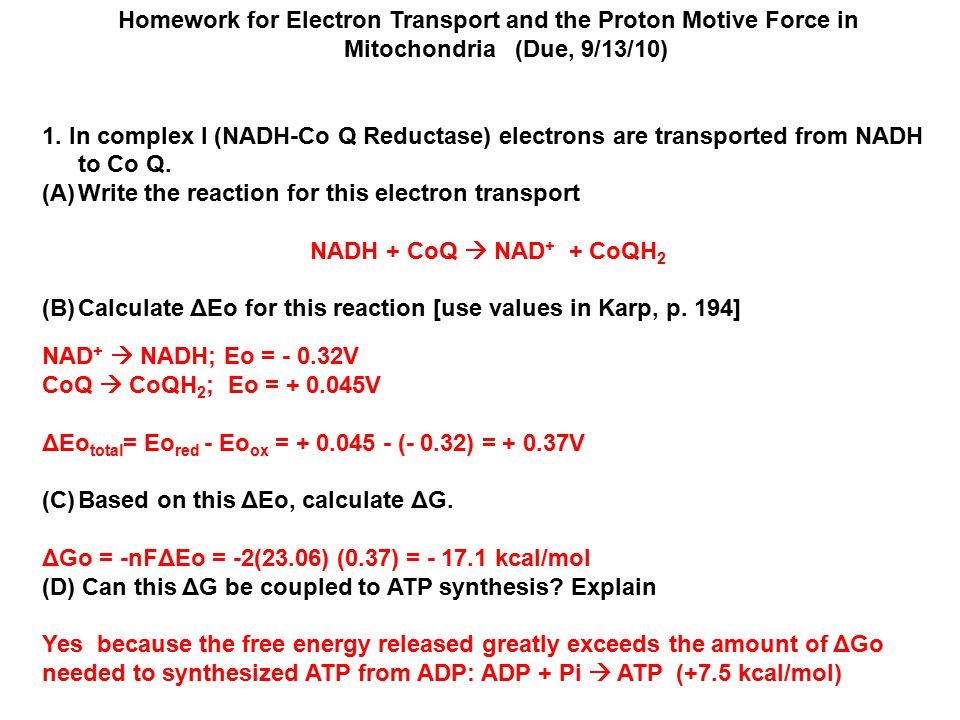
Homework For Electron Transport And The Proton Motive Force In Mitochondria Due 9 13 10 1 In Complex I Nadh Co Q Reductase Electrons Are Transported Ppt Video Online Download

Lecture 28 Oxidative Phosphorylation Flashcards Quizlet

The Proton Motive Force Chapter 21 Stryer Short Course Ppt Download

