Is used to produce NADH. Proton motive force and flagella proton motive force across thylakoid membrane proton motive force acidic proton motive force acid mine drainage.

Biofilms Flagella And Mechanosensing Of Surfaces By Bacteria Trends In Microbiology
Which of the following is false concerning carbon flow in the different pathways of energy yielding metabolism.

Proton motive force flagella. Basically this causes the cell to act like a tiny battery. Asked Aug 17 2019 in Biology Microbiology by Yellisima. Experimentally that rotation of the bacterial flagella motor requires a flow of protons across the cytoplasmic membrane the inner membrane of Gram negatives and that these protons essentially positive electricity flow through the MotAB of the stator ring which consists of a number of subunits which functions as proton channels.
Answer the following statement true T or false F molecular-and-microbiology. Carbon flow is from organic compounds. A proton motive force pmf Is used to synthesis ATP Is used to drive flagella rotation Is used to transport some substances All of the above A B 2.
Is used to drive flagella rotation. The cells move steadily along smooth paths run jump about briefly with little net displacement twiddle and then run in new directions. Is used to produce FADH2.
211 A Proton Gradient Powers the Synthesis of ATP The Chemiosmotic Theory Proposed by Peter Mitchell in the 1960s Nobel Prize 1978 The proton gradient generated by the oxidation of NADH and FADH 2 is called the proton-motive force. The proton-motive force powers the synthesis of ATP. They stop swimming when deprived of glucose.
This creates ATP while using the proton motive force created by. Each motor rotates a helical filament at several hundreds of revolutions per second hertz. Asked Oct 20 2015 in Biology Microbiology by Liberterian.
The proton-motive force created by the pumping out of protons by the respiratory chain complexes is in the mitochondria of most tissues mainly used to translocate protons through the ATP synthase complex leading to the formation of ATP from adenosine diphosphate ADP and phosphate. Here we show that flagellar secretion in Salmonella enterica requires the proton motive force PMF and does not require ATP hydrolysis by FliI. These results suggest that the FliH-FliI complex facilitates only the initial entry of export substrates into the gate with the energy of ATP hydrolysis being used to disassemble and release the FliH.
Furthermore proton motive force was essential for the export process. These results suggest that the FliHFliI complex facilitates only the initial entry of export substrates into the gate with. Is used to synthesize ATP.
In respiring bacteria under physiological conditions ATP synthase in general runs in the opposite direction. Its energy can either be used right away to do work like power flagella or be stored for later in ATP. It is powered by the flux of H or Na ions across the cytoplasmic membrane driven by an electrochemical gradient the proton-motive force or the sodium-motive force.
Proton motive force in flagella proton motive force in metabolism proton motive force location proton motive force thylakoid lumen loss of proton motive force. We conclude that the flagella are driven by a protonmotive force. Is used to synthesize ATP AND is used to drive flagella rotation.
The proton motive force occurs when the cell membrane becomes energized due to electron transport reactions by the electron carriers embedded in it. The bacterial flagellar motor is a reversible rotary nano-machine about 45 nm in diameter embedded in the bacterial cell envelope. Streptococcus strain V4051 is motile in the presence of glucose.
Bacteria use these gradients for flagella and for the transportation of nutrients into the cell. The export of several flagellar export substrates was prevented by treatment with the protonophore CCCP with. Archaeons power their flagella by proton motive force PMF whereas bacteria empower their flagella by ATP hydrolysis.
Furthermore proton motive force was essential for the export process.

Flagella Types Structure Movement
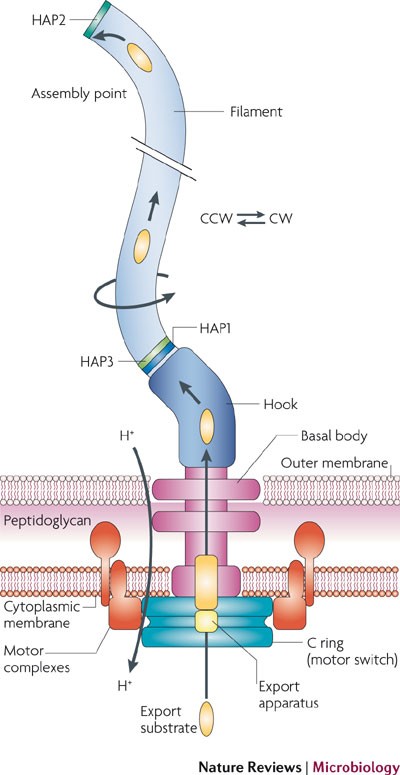
The Surprisingly Diverse Ways That Prokaryotes Move Nature Reviews Microbiology

Flagella Structure Arrangement Function Microbe Online
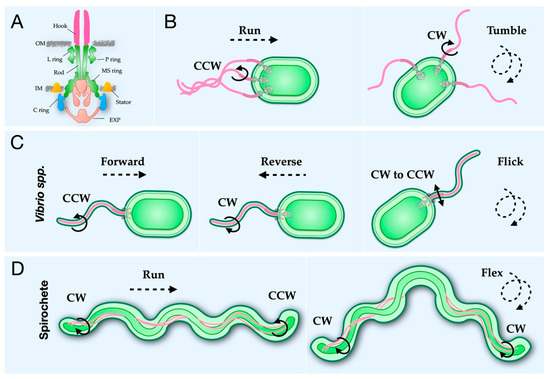
Biomolecules Free Full Text Structural Conservation And Adaptation Of The Bacterial Flagella Motor Html

Figure 1 From Probing The Dynamics Of The Proton Motive Force In E Coli Semantic Scholar

Schematic Diagram Of The Bacterial Flagellum The Flagellum Is A Download Scientific Diagram

Bacterial Flagella And Secretory Systems President S Dream Colloquium Simon Fraser University

Structure And Energy Conversion Mechanism Of The Bacterial Na Driven Flagellar Motor Trends In Microbiology

Rotation Of A Bacterium S Flagellum Is Driven By A Rotary Motor Download Scientific Diagram
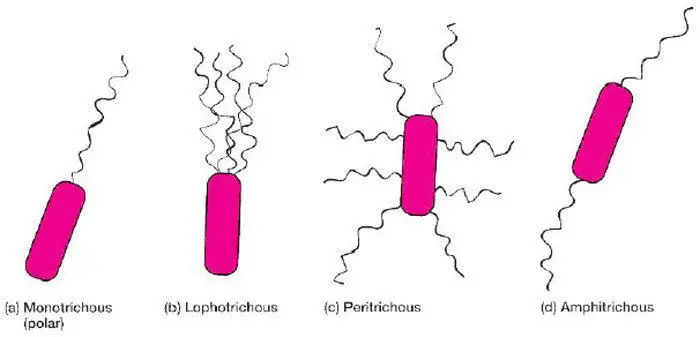
Flagella Structure Arrangement Function Microbe Online

The Bacterial Flagellum Rotary Nanomotor The Bacterial Flagellum Download Scientific Diagram
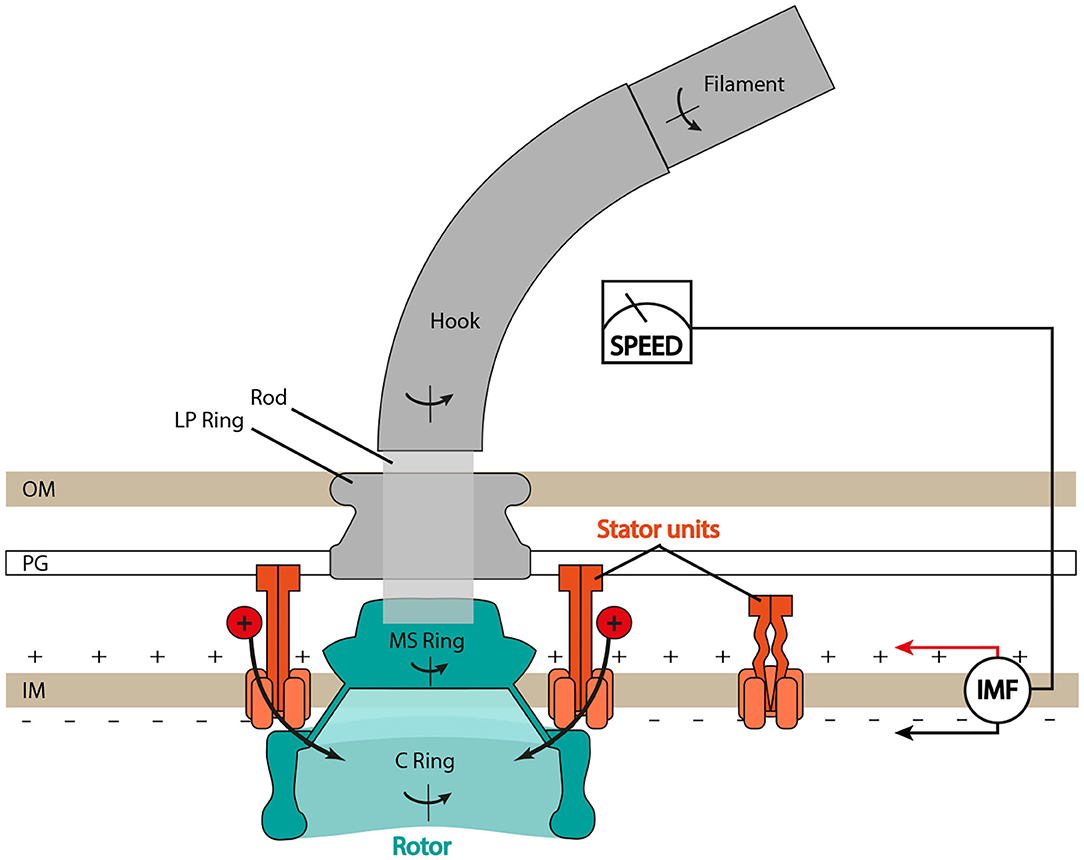
Frontiers The Dynamic Ion Motive Force Powering The Bacterial Flagellar Motor Microbiology

Sodium Powered Stators Of The Bacterial Flagellar Motor Can Generate Torque In The Presence Of Phenamil With Mutations Near The Peptidoglycan Binding Region Ishida 2019 Molecular Microbiology Wiley Online Library
Chapter 18 Oxidative Phosphorylation And Photophosphorylation

Insight Into The Flagella Type Iii Export Revealed By The Complex Structure Of The Type Iii Atpase And Its Regulator Pnas




